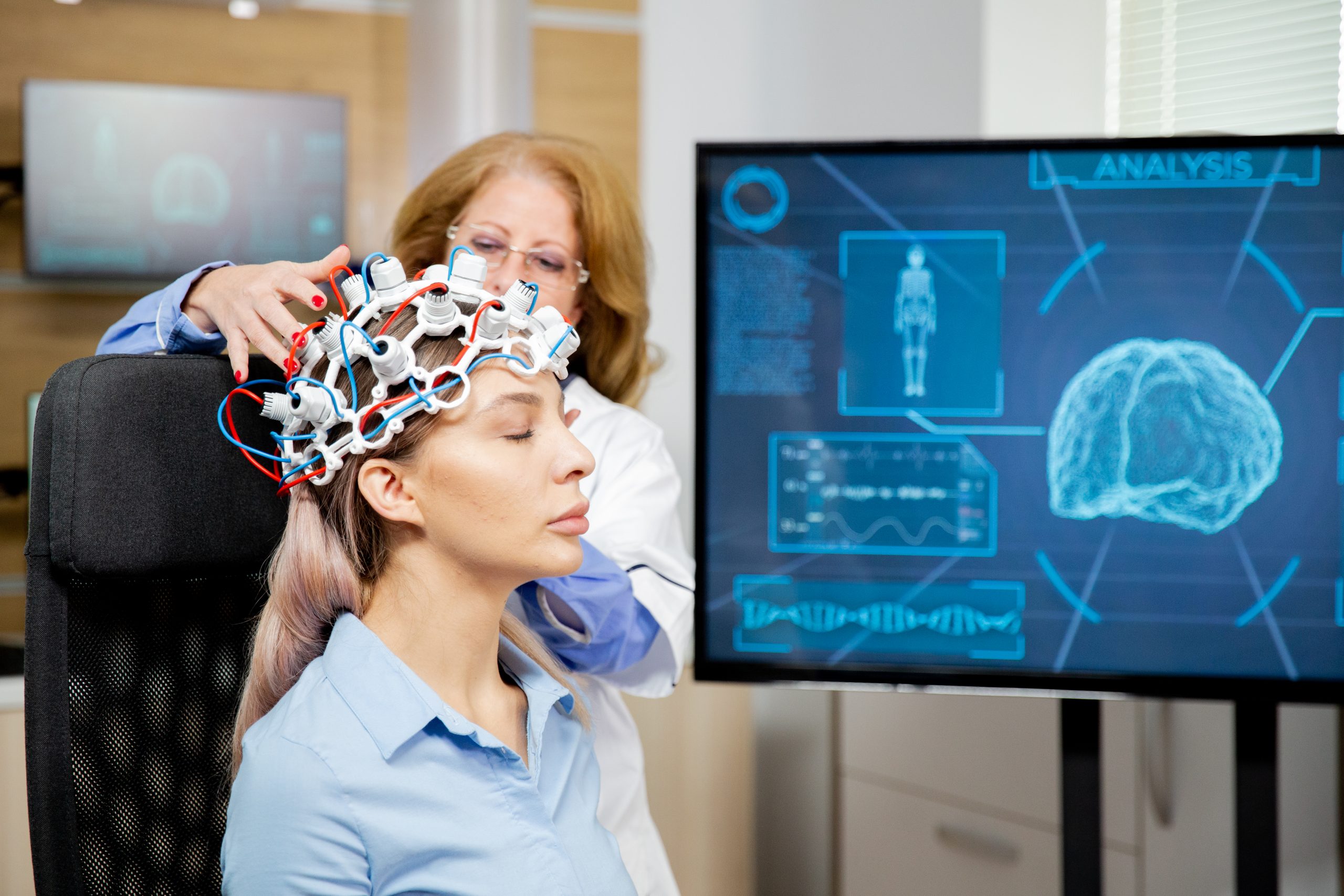
Many different techniques exist to read and analyse the functioning of the human brain. These techniques allow experts to directly observe human brain activities while subjects handle various motor, cognitive, or perceptual tasks.
Techniques and tools like EEG kits and fMRI combine functional brain imaging with data analysis techniques and experimental designs to examine the functions of brain regions and their respective interactions.
The enormous success of functional brain imaging techniques’ applications has led to the emergency of neuroeconomics, which is a nascent field. This nascent field has enhanced how scientists and researchers analyse human brain functioning and decision-making.
This comprehensive article explores three techniques used to analyse human brain functioning. They include:
- EEG
- fMRI
- MEG
Read on to unearth more about the world of human brain functioning analysis.
EEG: Electroencephalography
With this technique, you’re simply measuring and analysing electrical activity. The different cortical layers of the brain allow you to complete this task. This technique relies on electrical signals picked up from the brain’s grey matter regions. These regions contain a higher concentration of pyramidal cells that communicate with each other across human life.
Anytime enormous groups of these cells are firing up in a synchronised manner; the spawned electricity radiates to the surface of the scalp. This is what a 16 channel EEG kit or tool records with Electroencephalography electrodes. Since the electric fields are still lower, signals created are magnified.
The activity will be stronger than that of a reference location. You’ll receive insights into human brain processes with a high time resolution with EEG kits.
FMRI: Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
fMRI is also a popular and effective technique. It captures and measures human brain function. It works by detecting the changes in blood flow linked to neural activity. The idea behind this technique is that neurons require more oxygen. This is when they are active.
fMRI is a relatively slow neuroimaging technique. This is especially true when you compare it to:
- MEG
- EEG
But its excellent spatial resolution is the central strength. Users can construct independent skull shapes and cortical layers of their respondents.
MEG: Magnetoencephalography
MEG captures the magnetic fields produced by the neural activity. MEG tools are completely stationary. This is contrary to fMRI devices.
For optimal results, they require the participants to sit or lay almost motionless and keep their movements to a minimum. MEG blends the high spatial resolution with high temporal resolution, similar to EEG.
Of these three techniques, EEG is the most cost-efficient and versatile solution. You just need a high-quality 16-channel EEG kit to achieve the best results.